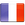
Helical Gears UK | High Precision Helical Gear Power Transmission
Helical Gears – Smooth and Efficient Power Transmission
A helical gear is a widely used gear type in modern mechanical engineering, valued for its smooth operation, load capacity, and durability. Unlike a spur gear, a helical gear features angled teeth that are cut at an angle to the axis of rotation, allowing gradual tooth engagement and improved performance.
Gears are most commonly used in systems where reliable power transmission and controlled motion are required, and helical gears are a preferred solution depending on the application.
What Is a Helical Gear?
A helical gear is a type of cylindrical gear (also described as a type of cylindrical) with teeth inclined at a specific helix angle. The helical gear is defined by this angle, which creates overlapping contact between teeth during rotation.
This design allows helical gears engage smoothly, transmitting torque with reduced shock loads when two teeth come into contact.
Helical Gear Geometry
The geometry of a helical gear is defined by several parameters:
- Number of teeth (for example 20 teeth or a small number of teeth)
- Pitch of a helical gear
- Pressure angle and reference pressure angle
- Working pressure angle
- Helix angle relative to the angle to the axis
- Center distance and center distance of a helical or distance of a helical gear
The involute tooth form ensures correct line of action and consistent contact at the point of contact along the tooth surface from the tooth tip inward.
Helical Gear Engagement and Mesh
In a helical gear pair, the gear teeth contact gradually, resulting in a higher contact ratio than spur gears. When two helical gears or a pair of helical gears are assembled, the pair of helical elements ensures continuous mesh and reduced load per tooth.
Compared with spur gears and compared to spur gears, this overlapping contact provides quieter operation and lower noise and vibration.
Direction and Orientation
Helical gears may be left handed helical or right-handed. In a set of helical gears, the mating gear must have the opposite hand to ensure proper direction of rotation.
A herringbone gear or double helical gears design eliminates axial forces by combining opposing helix angles.
Forces, Thrust and Bearings
While helical gears improve smoothness, they generate axial thrust in addition to radial loads. This thrust must be managed using appropriate thrust bearing solutions or thrust bearings to absorb axial forces.
The applied torque and transmitted load through the shaft affect bearing selection and bearing life.
Helical Gears vs Other Gear Types
When compared with spur designs, helical gears offer higher load capacity and smoother engagement. However, the disadvantages of helical gears include increased axial load, more complex manufacturing, and slightly higher losses due to sliding contact.
Compared to a worm gear, helical gears provide higher efficiency, while bevel gear or bevel solutions are used for intersecting shafts. Helical gears are also commonly integrated into planetary gear systems.
Manufacturing and Design Considerations
The design of helical gears requires precision and advanced processes such as gear hobbing using a dedicated gear hobbing machine and specialised cutter tools. Profile shift coefficients may be applied to optimise strength, reduce amount of backlash, or adapt to specific gear ratio requirements.
The driven gear and driving gear must be manufactured to ensure proper alignment, accurate center distance, and correct system helical gears interaction.
Precision and Lubrication
High-performance systems demand high precision gears and effective lubrication to protect the helical gear tooth surfaces. Proper lubrication supports durability, reduces wear, and maintains consistent performance over time.
Applications of Helical Gears
Helical gears transmit power efficiently in a wide range of applications, including:
- Industrial transmission systems
- Electric motor drives
- Heavy machinery and gearboxes
- Automotive and industrial equipment
Their high strength and smooth engagement make them ideal where reliability and comfort are essential.
Helical Gears in Power Transmission Systems
In modern mechanical systems, helical teeth enable smooth load transfer between gears. As the teeth engage, forces are distributed along the tooth length, reducing stress concentration.
For optimal results, gears must be correctly designed, manufactured, and installed to ensure proper alignment and long service life.
Why Choose Helical Gears?
With smoother engagement, reduced vibration, and high load capacity, helical gears remain one of the most effective solutions for demanding power transmission challenges. Their versatility allows engineers to balance efficiency, durability, and precision across many industries.
OUR SERVICES
Worms Gears, CNC Machining
CNC Turning, CNC Milling, Grinding, Boring, Drilling, Nitriding, Anodizing, Powder Coating, Galvanizing, Welding, Bending.
OFFICE HOURS
Monday-Friday 7:00 AM to 4:00 PM
OFFICE ADDRESS
SCHULTECH TECHNOLOGIES FOR INDUSTRY
SEBASTIAN SZULTKA
ul. Ułańska 7/201
40-887 Katowice Poland
TAX 6342452872
IDS 243364656
EORI 634245287200000
CONTACT
info@schultech.eu
+48 796 777 341
Privacy Policy
A website builder was used to create the site WebWave.